Last updated on May 4th, 2022 at 06:03 am
In back to the basics for TPMs, we will go over the differences between HTTP vs HTTPS. We will understand HTTP & HTTPS independently and then dive into the need for HTTPS. After which we will move into discussing where they are similar and where HTTPS adds value.
What is HTTP?
Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is a protocol for transmitting and receiving information across the Internet. HTTP serves as a request and response procedure that all agents on the Internet follow so that information can be rapidly, easily, and accurately disseminated between servers, which hold information, and clients who are trying to access it. You normally use HTTP when you are browsing the web, its not secure, so someone can eavesdrop on the conversation between your computer and the webserver. In many cases, clients may be exchanging confidential information with a server, which needs to be secured in order to prevent unauthorized access. For this reason, https, or secure http, was developed by Netscape to allow authorization and secured transactions.
HTTP is stateless. The lifetime of a connection corresponds to a single request-response sequence. The pure HTTP server implementation treats every request as if it was brand-new. HTTP pages are stored on your computer and internet caches. The pages load faster, but they are stored on systems that you potentially don’t have control over e.g.: ISP’s caching proxy. HTTP server, is implemented by Apache HTTP server, Microsoft IIS, Jigsaw, Zope, etc. HTTP can be implemented on top of any other protocol on the Internet, or on other networks.
Advantages of HTTP:
Its platform independent, which allows straight cross platform porting. No runtime support required to run properly, it can be used over Firewalls! It’s not connection oriented, there’s no need for network overhead to create and maintain session state and information.
Drawbacks of HTTP:
As I said earlier, it comes with some security concerns, like privacy is not there, anyone can see your content. Integrity is not there, so someone can easily alter with the content. HTTP is insecure as there’s no encryption methods for it. So, it’s subjected towards man in the middle and eavesdropping of sensitive information. There is also no authentication, so you will not have any clear idea with whom you are initiating a communication. Authentication is sent in the clear, anyone who intercepts the request and can know the username and passwords being used.
What is HTTPS?
HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol over Secure Socket Layer, or HTTP over SSL) is a web protocol originally developed by Netscape.
HTTPS = HTTP + SSL
HTTPS uses Secure Socket Layer (SSL) as a sublayer under its regular HTTP application layering.
HTTPS:
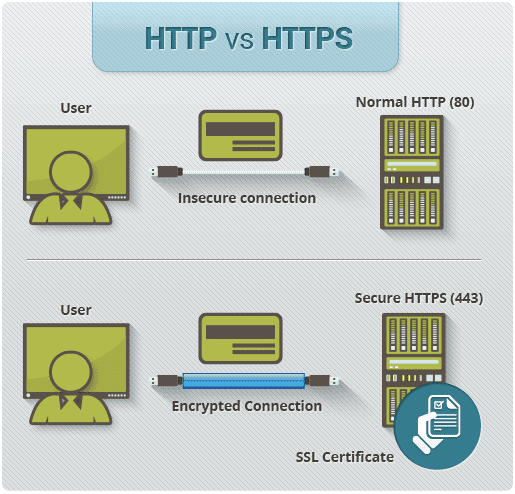
HTTPS stands for Hypertext Transfer Protocol over Secure Socket Layer or HTTP over SSL. In this SSL acts as a sub layer under regular HTTP application layering. HTTPS encrypts an HTTP message prior to transmission and decrypts a message upon arrival. By default, HTTPS uses 443 port, whereas HTTP use port of 80. URL’s beginning with HTTPS indicate that the connection between client and browser is encrypted using SSL.
For example: https://www.gmail.com
SSL transactions are negotiated by means of a key based encryption algorithm between the client and the server, this key is usually either 40 or 128 bits in strength, though higher number of bits indicates more secured transaction.
HTTPS or SSL connections are necessary if you have any online store or you do any financial transactions using credit card or online banking or ask for any other sensitive information.
Some of the advantage of HTTPS are like it offers Privacy, Integrity & Authentication which are missing in HTTP based connection. Though it have some drawbacks and they are like, HTTPS server can only provide one “virtual host” behind single socket. HTTPS cannot prevent stealing confidential information from the pages cached on the browser & HTTPS is quite slower compared to HTTP.
Similarity between HTTP and HTTPS:
In many ways, https is identical to http, because it follows the same basic protocols. The http or https client, such as a Web browser, establishes a connection to a server on a standard port. When a server receives a request, it returns a status and a message, which may contain the requested information or indicate an error if part of the process malfunctioned. Both systems use the same Uniform Resource Identifier (URI) scheme, so that resources can be universally identified. Use of https in a URI scheme rather than http indicates that an encrypted connection is desired.
Difference between HTTP and HTTPS:
1. URL begins with “http://” in case of HTTP while the URL begins with “https://” in case of HTTPS.
2. HTTP is unsecured while HTTPS is secured.
3. HTTP uses port 80 for communication while HTTPS uses port 443 for communication.
4. HTTP operates at Application Layer while HTTPS operates at Transport Layer.
5. No encryption is there in HTTP while HTTPS uses encryption.
6. No certificates required in HTTP while certificates required in HTTPS.
How HTTPS works ?
For HTTPS connection, public key and signed certificates are required for the server.
When using an https connection, the server responds to the initial connection by offering a list of encryption methods it supports. In response, the client selects a connection method, and the client and server exchange certificates to authenticate their identities. After this is done, both parties exchange the encrypted information after ensuring that both are using the same key, and the connection is closed. In order to host https connections, a server must have a public key certificate, which embeds key information with a verification of the key owner’s identity. Most certificates are verified by a third party so that clients are assured that the key is secure.
In other words, we can say, HTTPS works similar to HTTP but SSL adds some security to it.
HTTP includes the following actions:
- The browser opens a TCP connection.
- The browser sends a HTTP request to the server
- The server sends a HTTP response to the browser.
- The TCP connection is closed.
SSL will include the following actions:
1. Authenticate the server to the client.
2. Allow the client and server to select the cryptographic algorithms, or ciphers, that they both support.
3. Optionally authenticate the client to the server.
4. Use public-key encryption techniques to generate shared secrets.
5. Establish an encrypted SSL connection.
6. Once the SSL connection is established the usual transfer of HTTP requests will continue.
Where should HTTPS be used?
HTTPS should be used in Banking, Payment Gateways, Shopping Websites, Login Pages, Emails. For example:
Google Docs: https://docs.google.com
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/in/mariogerard/
Browser integration
Most browsers display a warning if they receive an invalid certificate. Older browsers, when connecting to a site with an invalid certificate, would present the user with a dialog box asking if they wanted to continue. Newer browsers display a warning across the entire window. Newer browsers also prominently display the site’s security information in the address bar. Extended validation certificates turn the address bar green in newer browsers. Most browsers also display a warning to the user when visiting a site that contains a mixture of encrypted and unencrypted content.
Recommended Reading :